Canada has been actively engaged in open banking initiatives, aiming to empower consumers with greater control over their financial data and enhance the sophistication and user-friendliness of financial applications. Despite the inherent benefits of open banking, progress in this initiative has been relatively slow. Simultaneously, the global economy is experiencing a slowdown, introducing new challenges for the banking sector.
This confluence of factors, including high-interest rates, a shrinking money supply, regulatory interventions, geopolitical tensions, and a new technology evolution, signifies a paradigm shift in the financial industry. In this context, this article explores the state of open banking in Canada in 2024 along with the obstacles.
The History of Open Banking in Canada and USA
The landscape of open banking is undergoing a shift in North America, with both the United States and Canada recently expressing their commitment to align with the demands of a rapidly evolving digital economy. In the United States, President Joe Biden’s executive order on competition, is set to usher in a new era by simplifying the process for consumers to switch banks. Under this directive, the Consumer Finance Protection Bureau is encouraged to craft rules, empowering customers of fintech firms and traditional banking institutions with the right to seamlessly port their financial data. This move signifies a departure from the traditional market-led approach in the U.S., reflecting a broader global trend of over 40 jurisdictions worldwide implementing open banking initiatives.
In Canada, a three-year consultation process culminated in the release of the Advisory Committee on Open Banking’s report, proposed an ambitious target of January 2023 for launching an open banking system. That time has come and gone. What sets the Canadian approach apart is its inclusive stance, extending the benefits of open banking not only to retail banking customers but also to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Things have moved slower than expected.
While North America has historically lagged behind in the open banking movement compared to regions like Europe and Asia-Pacific, the recent developments indicate a concerted effort to catch up with global counterparts.
The Role of Open Banking
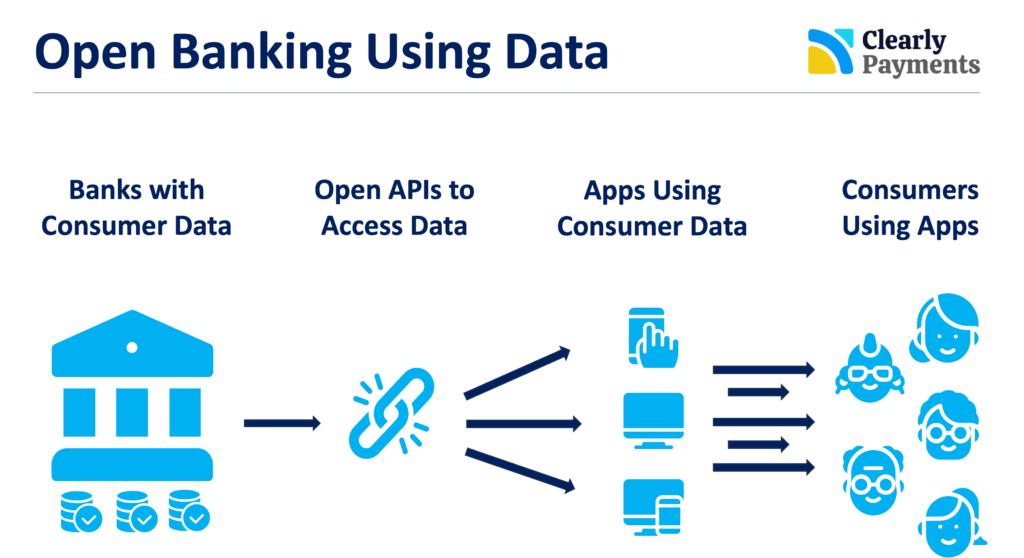
Open banking is about breaking down traditional banking silos and allowing consumers to share their financial data securely with third-party applications. This initiative aims to create a more interconnected and seamless financial ecosystem. By fostering collaboration between banks and Fintech companies, open banking enables the development of innovative financial products and services. This not only enhances consumer experience but also promotes healthy competition in the financial industry.
However, the pace of open banking adoption in Canada has been relatively sluggish. To fully unlock its potential, stakeholders, including regulators, financial institutions, and technology providers, need to collaborate effectively. Embracing open banking will not only position Canada as a forward-thinking financial hub but will also provide consumers with more control over their financial information and spur the development of advanced, user-friendly applications.
In a practical use case, consider a merchant leveraging the power of open banking to seamlessly integrate their business bank account with a financial management platform. This connection enables the platform to autonomously monitor the business’s income and expenses, presenting the business owner with invaluable insights into their financial performance. Beyond mere tracking, this integration lets the platform to generate comprehensive financial reports, efficiently manage cash flow, and facilitate informed decision-making for the business.
This scenario underscores the tangible benefits of open banking as a transformative tool for businesses of all sizes. By harnessing the capabilities of open banking, this small business owner not only optimizes the efficiency of financial management but also gains a holistic understanding of their financial landscape. The automated tracking of income and expenses serves as a foundation for robust financial reporting, providing the business owner with clear and actionable data.
Challenges in the Financial Sector & Economy
The global economic landscape has taken a turn for the worse starting in 2022, casting a long shadow over the banking industry. Traditional financial institutions, once considered bastions of stability, now find themselves navigating through difficult waters, grappling with a confluence of disruptive forces that threaten to reshape the very foundations of the sector.
At the heart of these challenges lies the global economic slowdown. The relentless tightening of monetary policy, driven by central banks’ efforts to combat soaring inflation, has sent interest rates skyrocketing. This abrupt surge in borrowing costs has thrown a wrench into investment decisions, stifled economic growth, and heightened the risk of recession.
Amidst this economic turmoil, banks face the daunting task of managing their liquidity positions effectively. The shrinking money supply, a consequence of central bank tightening, has made it more difficult for banks to access the funds they need to meet their obligations. This liquidity crunch has forced banks to scrutinize their lending practices, carefully assessing the creditworthiness of borrowers and potentially curtailing lending activity.
The regulatory landscape has also become increasingly complex, with governments introducing a barrage of new measures aimed at preventing systemic risks and protecting consumers. While these measures are well-intentioned, they have added a layer of bureaucratic hurdles for banks to navigate, diverting resources and increasing compliance costs.
Geopolitical tensions across the globe have further exacerbated the challenges faced by the banking industry. The ongoing conflicts and diplomatic standoffs have injected uncertainty into the global financial system, disrupting trade flows, unsettling investor sentiment, and threatening to trigger financial instability.
Tech Disruptions Like AI and Digital Currency
In the evolving landscape of financial services, institutions find themselves at the intersection of innovation and transformative technologies, with two prominent forces reshaping the sector: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and digital currencies. AI’s capacity to analyze extensive datasets is revolutionizing risk management, fraud detection, and customer service within the banking industry. Utilizing advanced algorithms, AI enables banks to discern patterns and anomalies in transaction data, offering a proactive approach to identifying potential risks and preventing fraud. Moreover, AI’s analytical capabilities extend to understanding customer behavior, facilitating the provision of personalized financial advice and tailored product offerings.
Simultaneously, the rise of digital currencies, encompassing cryptocurrencies and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), challenges traditional notions of currency and payment systems. Cryptocurrencies, characterized by decentralization and peer-to-peer transactions, promise faster, more cost-effective, and secure financial transactions. CBDCs, issued by central banks, provide a digital alternative to traditional fiat currencies, potentially enhancing financial inclusion, cross-border payments, and monetary policy.
To harness the opportunities presented by these transformative technologies, financial institutions must be adept at mitigating associated risks. This is both difficult and distracting for banks because it requires rapid change. While AI integration enhances decision-making, operational efficiency, and customer experiences, concerns regarding data privacy, algorithmic bias, and regulatory compliance must be addressed. Exploring the potential of digital currencies requires careful consideration of regulatory frameworks, security measures, and consumer education. Collaboration with regulators to establish clear guidelines ensures adherence to stringent security standards and consumer protection measures.
Banks need to move quickly because smaller and more nimble players are quickly developing new financial services. Many of these services will compete with traditional banking services. In navigating this technological landscape, banks can position themselves for future growth and success. Embracing innovation, fostering collaboration with regulators and fintech companies, and prioritizing consumer protection will enable banks to leverage the power of technology, enhancing operations, expanding their reach, and defining the future of finance.
Financial Institutions Need to Adapt
In the face of these challenges, the call for change and evolution in the financial sector becomes imperative. Financial institutions must reassess their strategies and embrace a proactive approach to remain resilient in an ever-changing environment. One of the significant drivers of change is the slow but steady progress of open banking initiatives in Canada. Open banking is not just a regulatory requirement; it is a catalyst for innovation and customer empowerment.
In the midst of a shifting economic and technological landscape, the Canadian banking sector finds itself at a crossroads. Open banking initiatives represent a key step towards fostering innovation and empowering consumers. Financial institutions must not only navigate the challenges posed by the global economic slowdown but also harness the transformative potential of technologies like AI and digital currencies. By embracing change and fostering collaboration, the Canadian banking industry can position itself as a resilient and adaptive force in the evolving global financial landscape.